What are the Taxes a Small Business Needs To Pay? Info Plus Forms And Deadlines.
Sole proprietorship is a kind of business set-up wherein the owner is only owned by one individual. Sometimes it is described as a ‘pass-through’ structure as the entirety of the business such as income and expenses, assets and liabilities are pass through the individual income tax return or the ITR. This also means that the personal Tax Identification Number or the TIN of the person and his or business are just one.
This also holds true if you are an independent professional, a freelancer, a self-employed or is engaged in a small business. The bottom line is that you just need to register your business and/or services offered so invoices and receipts can be issued. Also, it would be beneficial if expenses receipts are kept and monitored so true net income will be determined.
Lastly, the most important of all of these is the filing of the applicable taxes either monthly, quarterly and annually. Below are the descriptions of the taxes that should be filed and their corresponding details and payment deadlines so you will not become a delinquent tax payer. Remember, not paying the necessary taxes are punishable by law and is a criminal offense.
Percentage Tax (Monthly and Quarterly)
This is a business tax imposed on persons or entities and or transactions who (1) sells or lease goods, properties or services in the course of trade or business and are exempt from value-added tax (VAT) under Section 109 (w) of the National Internal Revenue Code, as amended, whose gross annual sales and/or receipts do not exceed Php 1,919,500 and who are not VAT-registered; and (2) those who engaged in the identified industries by the BIR.
Moreover, below is a summary of the monthly and quarterly payments with deadlines, forms used and documentary requirements for percentage tax.
Monthly Percentage Tax
- BIR Form 2551M – Monthly Percentage Tax Return. Filed within twenty (20) days following the end of each month. Computed as sales tax that is equivalent to 3% of monthly gross sales.
The documentary requirements are as follows (1) duly issued certificate of creditable tax withheld at source (BIR Form 2307), if applicable (2) duly approved tax debit memo, if applicable (3) for amended return, proof of payment and the return previously filed (4) authorization letter, if filed by an authorized representative.
Quarterly Percentage Tax
- BIR Form 2551Q- Quarterly Percentage Tax Return. Filed within twenty (20) days after the end of each taxable quarter. This reports the three (3) months income of a particular quarter.
The documentary requirements are as follows (1) duly issued certificate of creditable tax withheld at source (BIR Form 2307), if applicable (2) duly approved tax debit memo, if applicable (3) for amended return, proof of payment and the return previously filed (4) authorization letter, if filed by an authorized representative.
2. Quarterly Income Tax
This refers to your individual income tax. This means that as a sole proprietor or a self-employed, the income you generate from your business is subject to a graduated income tax that range from a minimum of 5% to a maximum of 32% which is payable every quarter. However, if you incorporate your business, you automatically pay the fixed 30% corporate income tax. The form used is BIR Form 1701Q – Income Tax for the quarter and is filed on or before the 60th day after the close of each quarter.
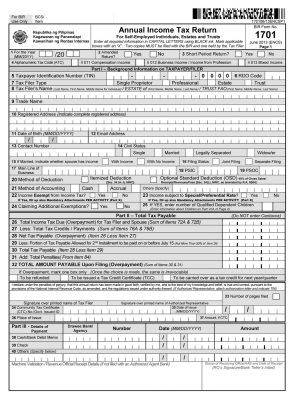
3. Annual Income Tax
This is based on your net income for the preceding year. The form used is BIR Form 1701 – Annual Income Tax Return and is due every April 15 of each year.
4. Withholding Taxes
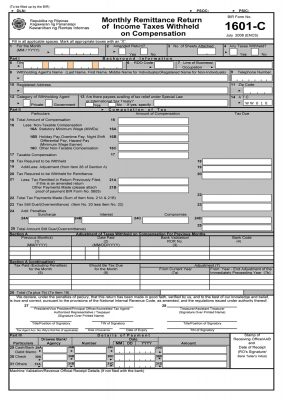
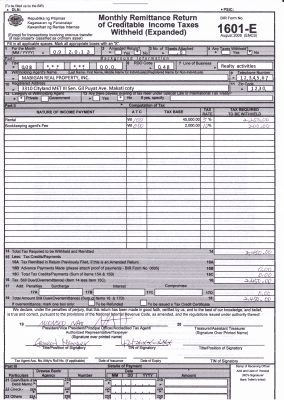
This is applicable only to those small businesses with salaried employees and third party contractors and this also includes lessors for office rent. Withholding taxes can be in a form of expanded, compensation and final. The forms used are BIR Form 1601C – Monthly Remittance Return of Income Taxes Withheld on Compensation and/ or BIR Form 1601E – Monthly Remittance Return of Income Taxes Withheld (Expanded). Whatever form it is, this is due on or before the 10th day of the month following the month the withholding was made.
It is also important to emphasize that the business needs to renew licenses and permits with the local government units annually. This is due on or before the 20th of January of each year.
Penalties and Fees
Take note also that penalties are automatic as soon as you have not complied with all the taxes due mentioned above. The details of these penalties are as follows:
(1) a surcharge of 25% for failure to file and/or pay any internal revenue tax at the time or times required by law or regulation.
(2) a surcharge of 50% in case a false or fraudulent return is willfully made.
(3) interest at the rate of 20% per annum on any unpaid amount of tax from the date prescribed for the payment until it is fully paid.
(4) compromise penalty.
Lastly, to ensure a smooth business operation, there is a need to be conscious and mindful of the taxes that are going to be filed so business will be good.







If my husband is currently working in a big company and also owned a small kart (lemonade stand) how do we file ITR? Also we only started our kart last march 27, 2017 . This is our 1st business so we don’t really know what to do
How to apply for a business permit? Planning to have my food cart business on mall
when paying quarterly tax.. do i need to pay for the signing of cpa every quarter? my business is excemted for quarterly charges tax.. it is required to be signed by a cpa?
This is the perfect website for anyone who really wants to undestand this topic.
You realize sso much its almost tough to argue with you
(not that I personally would want to…HaHa).
You certainly puut a brand new spin on a subject that’s bee written aboht for decades.
Great stuff, just wonderful!
Sole Proprietor can BIR receipts/invoice send abroad ?
Does it need to file personal ITR yearly even though theres already 1701 and 1701Q in every branch
If employees are below minimum wage ngre repair lng ng damit, and no taxes were deducted on their weekly salary, does it still need to file 1601C
They’re exempted from paying taxes
Thank you very much! I’m helping a friend who’s working for a small business. Your article helped greatly! It is so well-organized and short. Thus, i understand it easily. Daghang salamat!
Hello just want to ask what if annually you earned less than 250,000 am I exempted in paying taxes? And if not what are the things I need to pay monthly or any fees? Thank you
OMG! Thank you so much for this article. It is very well written and informative. I hope you continue to share your words and knowledge for students like me.
Thank you so much for this article. Big help